Introduction
Occupant Classification Systems (OCS) are the unsung heroes behind smarter, safer buildings and vehicles. They detect, classify, and track people inside spaces to power use-cases like adaptive HVAC, personalized infotainment, safety restraints, energy savings, access control, and occupancy analytics. Recent advances in sensors and machine learning (ML) have transformed OCS from simple presence detectors into intelligent systems that understand who is where, doing what, and sometimes even how comfortable they are. This guide walks through the full lifecycle of modern ML-driven OCS: sensors and data, model choices, preprocessing and features, evaluation, deployment, privacy and safety, plus practical tips and future directions.
Definition
An Occupant Classification System (OCS) is a safety technology in vehicles that uses sensors – typically in the passenger seat – to detect the presence, weight, and sometimes the position of an occupant. Its primary purpose is to determine whether and how the passenger airbag should deploy in a crash, helping prevent injury to children or smaller passengers by suppressing or adjusting airbag activation when appropriate.
Why OCS matter today
OCS enable:
- Energy efficiency: HVAC and lighting can respond to real-time occupancy and activity levels rather than static schedules.
- Safety: In vehicles, OCS verify seat occupancy and classify occupant size and posture to optimize airbag deployment and restraint strategies.
- Personalization: Buildings and vehicles can automatically adjust lighting, temperature, and content based on who’s present.
- Analytics & operations: Facility managers and fleet operators gain actionable insights about space usage and patterns.
Machine learning makes these capabilities robust in the face of noisy sensors, varied human behavior, and complex environments.
Sensors and data sources
Modern OCS combine multiple sensing modalities to increase reliability:
- Cameras (RGB / IR / stereo): Rich spatial and appearance information; useful for pose, identity-less classification, and semantic understanding.
- Depth sensors / LiDAR / time-of-flight: Provide 3D shape and distance; excel at differentiating people from objects and estimating pose without detailed appearance.
- Pressure mats and seat sensors: Common in vehicles and chairs for direct contact detection and weight estimation.
- Ultrasonic and PIR sensors: Low-cost presence detection and coarse movement cues.
- Microphones / acoustic sensors: Can aid activity recognition and presence detection but raise privacy concerns.
- Wearables / BLE / UWB beacons: Offer identity and fine-grained localization when users opt-in.
Fusing modalities increases accuracy and robustness to occlusion, lighting changes, and adversarial scenarios.
Data collection & labeling
High-quality labeled data is the backbone of ML-based OCS.
- Scenarios: Collect in representative environments (day/night, varied clothing, different seating postures, with objects). For vehicles, include crash-relevant poses and varied occupant ages/sizes.
- Labels: Typical labels include presence/absence, seat occupancy, occupant type (adult/child/pet), posture (upright/reclined/forward), activity (sitting/standing), and anonymized identity clusters if personalization is needed.
- Annotation tools: Use bounding boxes, segmentation masks, depth annotations, and pose keypoints. For privacy, consider label-only approaches that never store raw images long-term.
- Class balance: Ensure minority classes (children, pets, rare postures) are represented – oversample or synthesize when necessary.
Synthetic data and simulation (e.g., rendered people in virtual cabin environments) can help cover rare or safety-critical situations.
Preprocessing & feature engineering
Raw sensor data must be normalized and converted into ML-friendly representations.
- Image preprocessing: Resize, normalize, handle exposure variations; apply data augmentation (flips, brightness, occlusion patches) to increase robustness.
- Depth/point-cloud processing: Voxelization, downsampling, normal estimation, or converting to depth images.
- Temporal features: Use motion cues and short-time windows to capture gestures or posture changes.
- Handcrafted features vs learned features: For resource-constrained devices, lightweight handcrafted features (HOG, silhouette descriptors, seat-pressure summaries) may suffice. For best accuracy, learn features end-to-end with CNNs or point-cloud networks.
- Sensor fusion: Align modalities in time and space (calibration). Combine at feature-level (concatenate embeddings) or decision-level (ensemble voting).
Model architectures
Model selection is driven by accuracy, latency, compute constraints, and privacy.
- Classical ML: Random Forests, SVMs, and Gradient Boosted Trees perform well with structured sensor features (seat pressure, PIR) and are lightweight to deploy.
- Deep learning (vision-centric): Convolutional Neural Networks (ResNet, MobileNet variants) for images; lightweight backbones (EfficientNet-lite, MobileNetV3) for edge devices.
- Temporal models: LSTMs, GRUs, or Temporal Convolutional Networks (TCNs) to model short-term dynamics. Transformer-based architectures are gaining ground for multimodal temporal fusion.
- 3D & point-cloud models: PointNet/PointNet++ and voxel-based 3D CNNs for depth/LiDAR.
- Multimodal fusion networks: Early, mid, or late fusion strategies to combine RGB, depth, pressure, and audio streams.
- TinyML: Quantized and pruned models, knowledge distillation, and hardware-aware neural architecture search for microcontroller deployment.
Choose models that meet the target device’s inference time and power budgets while satisfying safety/performance constraints.
Training, evaluation & safety metrics
Robust training and evaluation are crucial.
- Losses & objectives: Cross-entropy for classification; weighted losses when classes are imbalanced; multi-task losses when predicting occupancy + posture simultaneously.
- Metrics: Accuracy, precision/recall, F1, confusion matrices per seat/zone, area under precision-recall curve (for imbalanced tasks), latency and memory usage, and safety-critical false negative rates (e.g., failing to detect a child in a vehicle seat).
- Validation strategies: Cross-validation across environments and users; holdout test sets containing rare but critical scenarios.
- Adversarial testing: Evaluate robustness to occlusion, low-light, spoofing (e.g., mannequins), and sensor failure.
- Calibration & uncertainty: Use calibrated probabilities, Bayesian approaches, or ensemble variance to express model confidence – important for safe fallbacks.
Deployment & system integration
Deployment considerations often determine the final architecture.
- Edge vs cloud: Edge reduces latency and preserves privacy; cloud enables heavier models and aggregation but needs secure communication and handles connectivity issues. Hybrid architectures are common.
- Real-time constraints: Prioritize low-latency models for safety-critical functions (e.g., airbags).
- Fallbacks & safety policies: Define conservative fallback behaviors when confidence is low (e.g., assume occupied, trigger alerts).
- Over-the-air updates: For model improvements and security patches—implement secure update mechanisms and validation.
- Monitoring & drift detection: Continuously monitor model performance and sensor health; set up triggers for retraining when distribution shift is detected.
Privacy, ethics and regulation
OCS often process sensitive information – approach with care.
- Privacy-preserving design: Favor depth-only sensing for similar performance without storing identifiable RGB images; apply on-device inference and ephemeral buffering.
- Data minimization: Store only necessary features/aggregates and delete raw sensor data when not required.
- Consent & transparency: Inform users about what’s collected and offer opt-outs. For vehicles, ensure compliance with regional safety and privacy regulations.
- Bias & fairness: Test across demographic groups and seating conditions to avoid systematic misclassification, especially for child/pet detection and size estimation.
Challenges and future directions
Key challenges include robust generalization in diverse environments, low-cost sensing for wide adoption, and balancing personalization with privacy. Promising directions: multimodal transformer models, continual learning for on-device personalization, synthetic-data-driven safety testing, and standardized benchmarks for OCS performance.
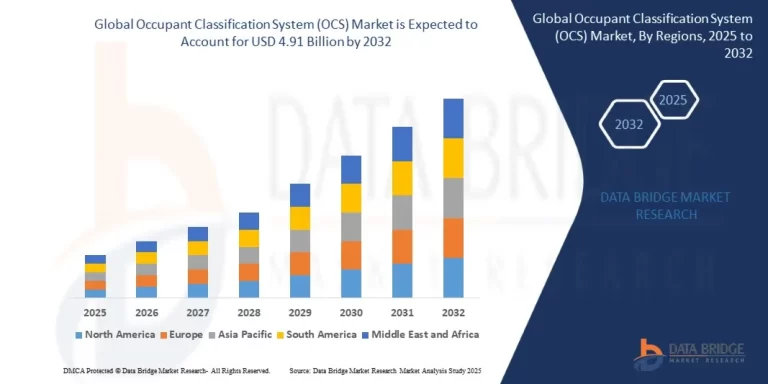
Growth Rate of Occupant Classification System (OCS) Market
According to Data Bridge Market Research, the occupant classification system (OCS) market was estimated to be worth USD 3.08 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.01% to reach USD 4.91 billion by 2032.
Learn More: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-occupant-classification-system-ocs-market
Conclusion
Machine learning has turned OCS into powerful enablers for safety, efficiency, and comfort. Building a reliable OCS requires thoughtful sensor choice, careful data collection, appropriate model selection, rigorous testing for edge cases, and strong privacy safeguards. With attention to these elements, OCS can deliver smart behavior that’s accurate, fair, and respectful of users – powering the next generation of intelligent spaces and vehicles.